旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem,TSP)是一个经典的组合优化问题。经典的TSP可以描述为:一个商品推销员要去若干个城市推销商品,该推销员从一个城市出发,需要经过所有城市后,回到出发地。应如何选择行进路线,以使总的行程最短。
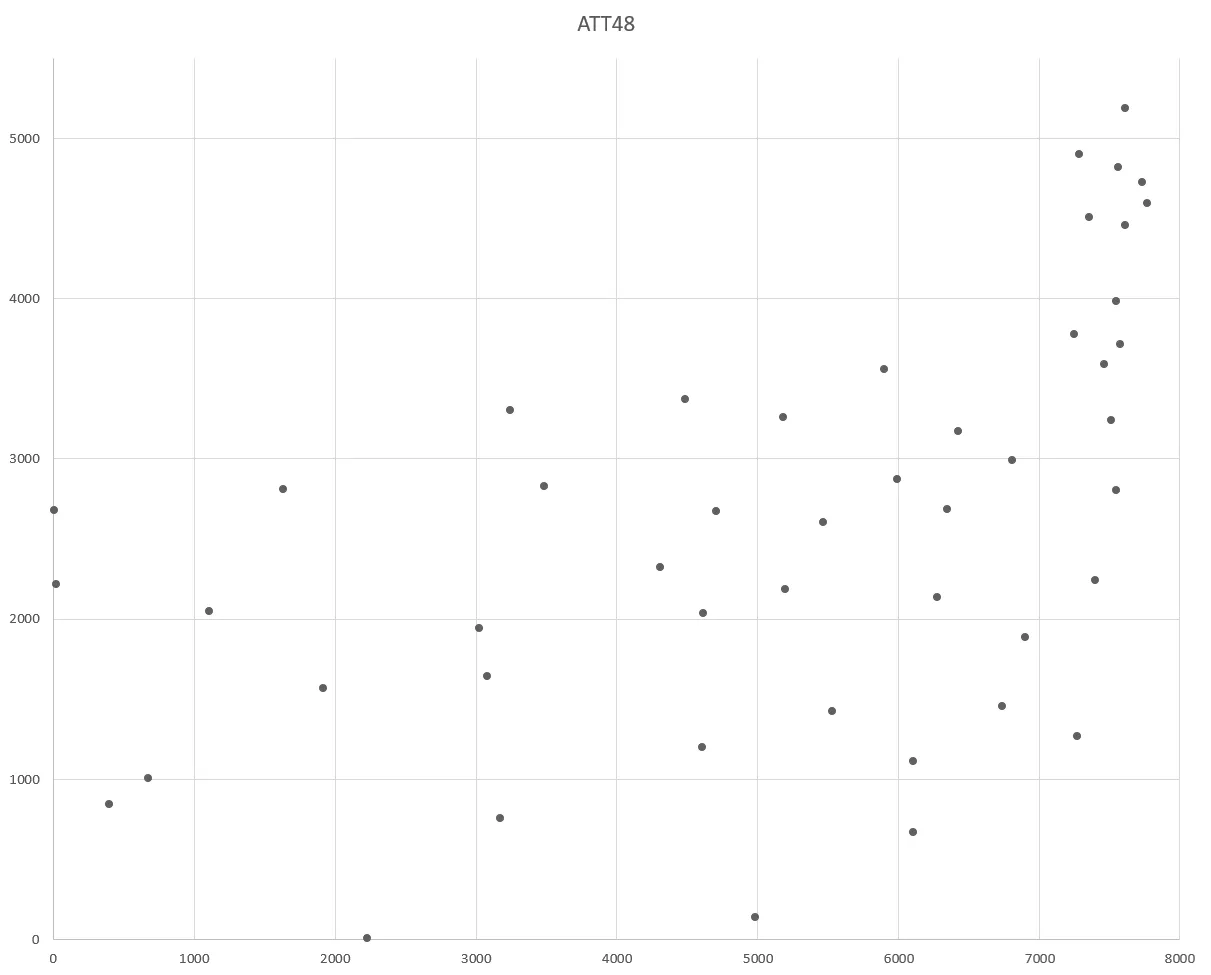
在本文中使用的数据为来自TSPLIB的ATT48,即美国本土48个州首府坐标,TSPLIB的已知最优解为10628。
从图论的角度来看,该问题实质是在一个带权完全无向图中,找一个权值最小的Hamilton回路。由于该问题的可行解是所有顶点的全排列,随着顶点数的增加,会产生组合爆炸,它是一个NP完全问题。
解决思路
由于NPC问题至今没有得到解决,TSP问题往往是通过启发式搜索(我觉得也可以叫暴力)算法来“猜”出最优解。
使用遗传算法来解决TSP问题,主要思路如下:
- 使用一个不重复的,首尾相同的字符串来表示一个解,该字符串即TSP的顺序
- 使用交叉,变异两种方式产生新的解,并根据数据来计算解的适应度
- 种群定义为当前所有解的一个集合,当种群中的每个个体完成一次“进化”(由概率决定)之后,称之为进化一代
- 对每一代种群进行筛选(根据适应度进行排序),择优劣汰,具有更优秀适应度的个体有更高的概率被其他个体选中进行交叉
- 不断重复上述过程,直到出现可以完全适应的个体(最优解)
遗传算法在TSP问题上可以融合多种算法,从而达到不同的效果,比如交叉应该如何交叉,变异应该如何变异等等。同时遗传算法的参数难以调整到最优——包括交叉率,变异率,种群容量等可以对搜索过程产生较大影响的参数都难以调整。限于个人水平,我无法从数学上给出最优参数,只能以经验论,加以多次实验选取表现优秀的样本。
解决方案
语言:C++
个体(解)的表示:用vector储存,代表节点遍历顺序
距离的计算:取伪欧式(pseudo Euclidean)距离,计算方法如下(向上取整):
$$
dist=\lceil{\sqrt{\frac{ {(X_1-X_2)}^2+{(Y_1-Y_2)}^2}{10} } }\rceil
$$
使用unordered_map(C++11),内部实现为散列表,使得计算个体适应度可以达到$O(N)$级别的复杂度
随机数的生成:设置时间种子,并由此生成随机数
交叉对象的选择:轮盘赌
交叉算法的选择:顺序移位
变异算法的选择:顺序移位 / 贪婪倒位
参数的选择:由多次实验得出
如何选择参数
可以对结果产生较大影响的参数有如下几种,分别对其进行测试。
适应度
已知ATT48的最优解为10628,若要使种群最优的个体得到更多被选择的机会,必定要使靠近最优解的个体拥有更大的适应度,并且越接近最优解得到的适应度越大(非线性关系)。
综上所述,我选择了如下的适应度计算方式:
$$
F_{适应度}=\frac{1}{distSum-10627}
$$
其中$distSum$为当前个体的距离总和,也就是当前解。
下面的测试均使用该适应度算法
种群容量
取交叉率为0.5,变异率为0.1,分别对种群容量10,20,50,100,150,200,500,1000进行实验,每组对解达到40000及以下时的代数与时间进行测试,3次取平均值,所得数据如下:
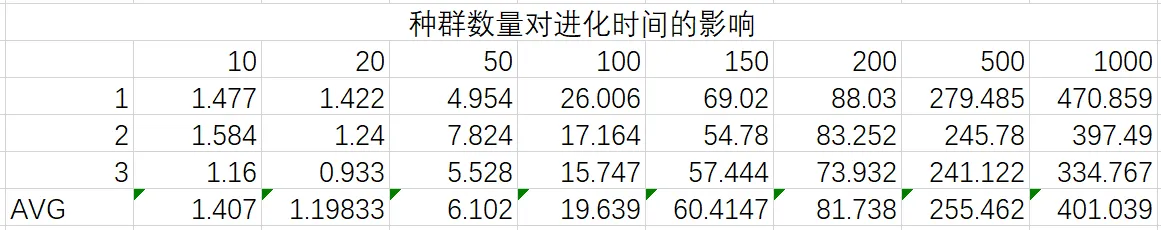
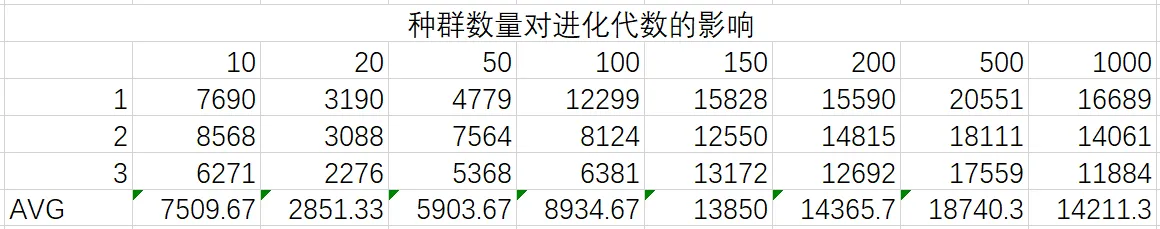
通过观察数据可以得出以下结论:
- 种群容量较小时,解可以很快地到达一种较优的状态
- 随着种群容量的增加,进化需要的时间代价会逐渐增加
- 种群容量过小时会种群会很快进入局部最优状态,这时候只能依靠变异来使种群进一步进化,效率是非常低的
那么,使用GA这类梯度下降算法时如何才能解决局部最优问题呢?
为了能在适当的时机跳出局部最优的陷阱,我在细胞培养中的传代培养得到了些许灵感,对传统遗传算法进行了一些小改进——一种自适应的种群容量自动扩增机制:
$$
packNum_{扩增}=packNum_{当前}×\lg{packNum_{当前}}
$$
- 设置初始种群容量上面实验表现最优的20,但是这种方式毕竟也算指数级增长,会很快达到一个不可用的数值,因此设置了一个Hayflick界限来表示最大传代次数
- 每次传代保留当前种群中最优秀的个体,他将作为普罗米修斯(Prometheus)将火种传递到新世界(扩增并随机生成的种群)
- 每次传代后停止判断与N代前是否重复,直到新种群趋于稳定时(种群最优值发生改变)重新激活统计
通过自动扩增的种群容量,可以兼顾小种群进化快与大种群进化稳的优点,达到快速进化的目的。
下面的测试均使用该自动扩增算法
交叉率
取变异率为0.1,种群容量为自动扩增,对交叉率0.1 ~ 1.0,以0.1为步距进行测试,记录10000代为止得到的最优解,每组测试10次取平均值,所得数据如下:
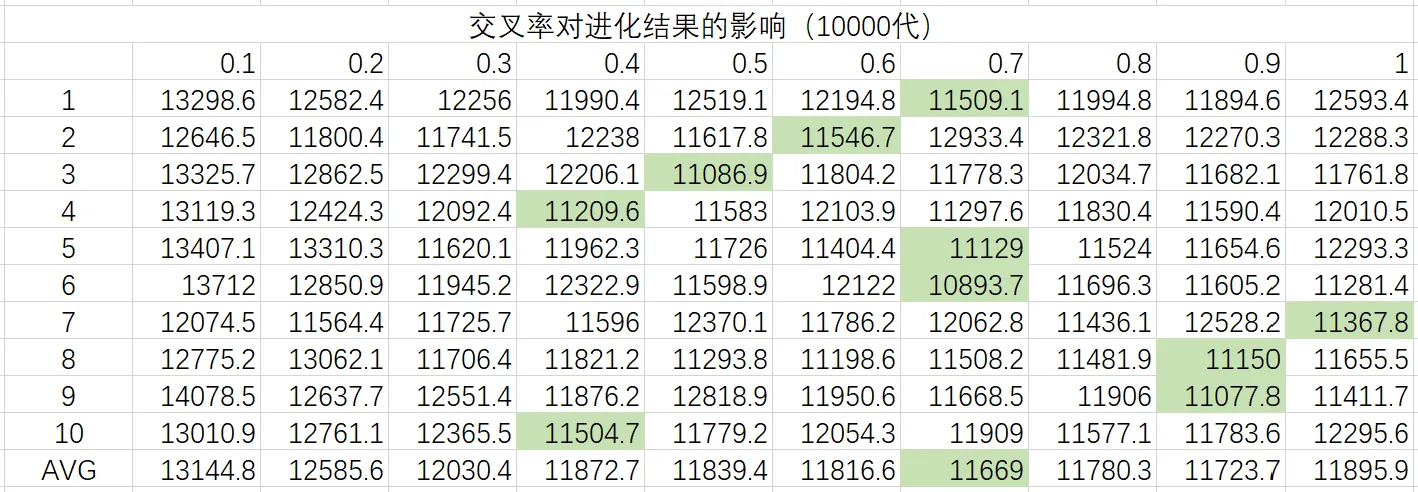
由实验数据可以得出优秀的交叉率集中在0.7附近,因此选取交叉率为0.7,即每个个体每代有70%的概率进行交叉。
变异率
取交叉率为0.7,种群容量为自动扩增,分别对变异率0.01,0.05,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5,0.7,0.9进行测试,记录10000代为止得到的最优解,每组测试10次取平均值,所得数据如下:
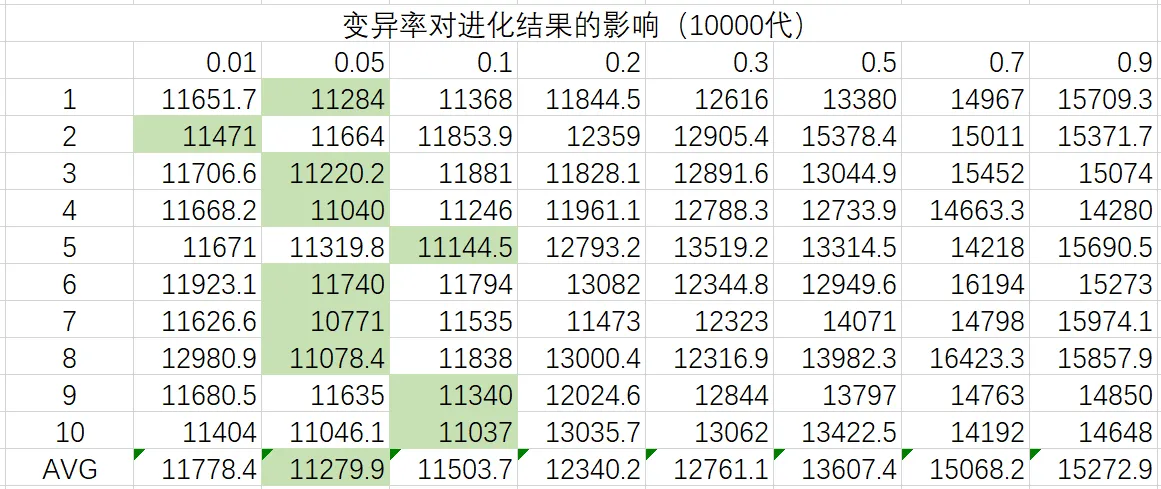
由实验数据可以得出,种群进化的情况随着变异率的逐渐增加而变差,优秀的变异率集中在0.01至0.1之间,因此对该部分的变异率再次分组进行实验,每组测试20次并将测试结果排序后去除最高的3个样本和最低的2个样本,取平均值,所得数据如下:
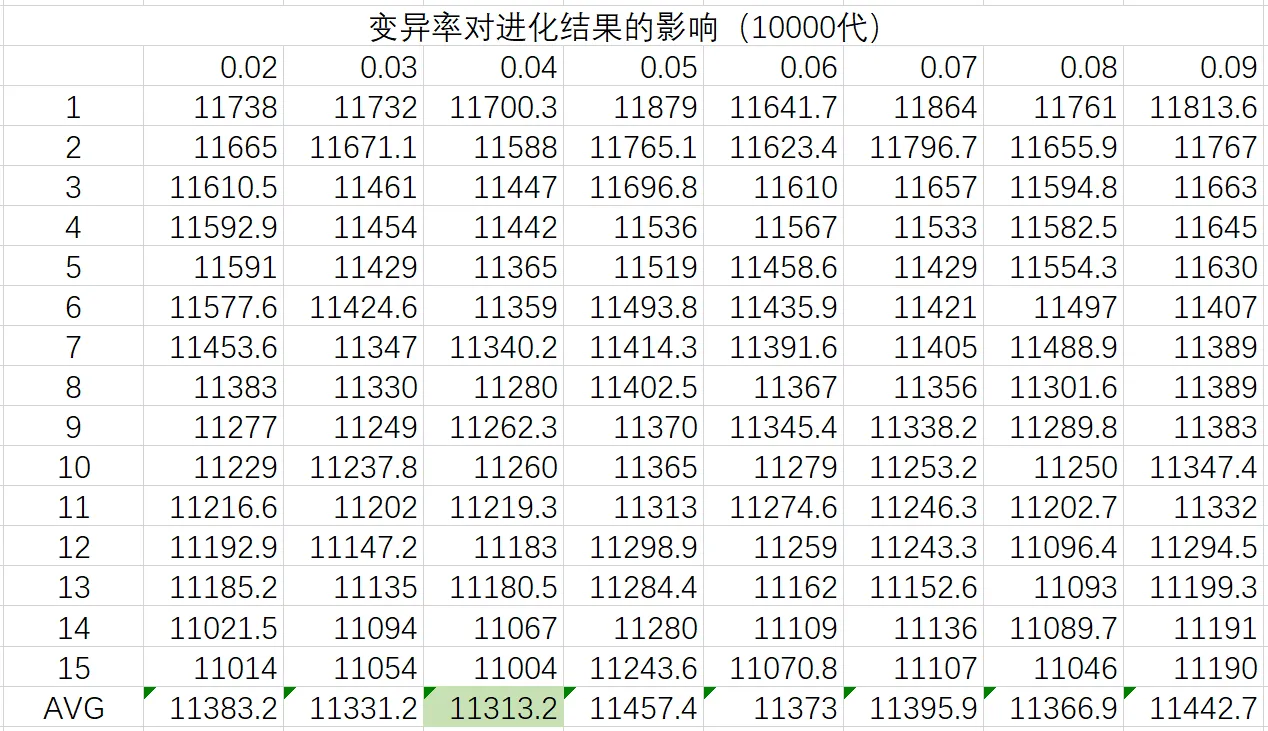
综合比较实验数据,可以认为变异率在$10^{-2}$这个数量级上的改变对进化的作用并不是特别明显,因此选取0.04作为变异率进行接下来的实验,即每个个体每代有4%的概率进行变异。
贪心初始化
由于随机初始化的结果偏离最优解过多,很大程度上会影响进化效率,因此在第一次初始化种群时,使用贪心算法的思路来选取第一个个体。
- 将起点压入栈,同时将起点标记为已访问,进行如下循环:
- 找出未访问过的,与栈顶元素距离最短的点
- 将该点压入栈,并标记为已访问
- 将终点(即起点)压入栈
通过贪心初始化的初始状态最优解只有随机序列的30%左右,极大地优化了进化效率。
变异算子
常规的交叉变异算法有很多种,包括顺序移位等
顺序移位交叉算子
在个体的序列中随机选择一个城市A和一个长度L
- 若$I_A+L<I_{end}$,则选定段$[I_A, I_A+L]$
- 若$I_A+L\ge I_{end}$,则选定段$[I_A, I_{end}]$
将选定段移至首部,剩余部分依次填入空缺处
但是由于该变异算子与交叉算子较为相似,并不能起到很好的变异效果。
在这里我参考了卞峰的《求解TSP的改进QPSO算法》一文,借鉴了其中的贪婪倒位变异算子并应用于该算法中。
贪婪倒位变异算子
在个体的序列中随机选择一个城市A,遍历找到距离城市A最近的城市B:
- 若B在A的左侧,则将$[I_B, I_A)$部分倒序
- 同理,若B在A的右侧,则将$(I_A, I_B]$部分倒序
经实验发现该算子比起之前应用的顺序移位算子在效率上虽然有些许降低,但是对于陷入局部最优的种群来说,有更大的可能性使种群继续进化。
综合两种变异算子的特点,将变异写成了一种自适应的模型:
- 初始状态使用顺序交叉算子,直到种群陷入局部最优,触发传代培养方法
- 此时通过判断条件变更算子,使用贪婪倒位继续进行搜索,并增大变异率
实验记录
- 实验样本:ATT48@TSPLIB
- 理论最优解:10628
- 实验平台:CLion 2019.3(G++ 8.2.1 x64)
1000代
| 序号 |
最优解 |
耗时 / s |
| 0 |
12530 |
0.871 |
| 1 |
11965 |
1.061 |
| 2 |
12571 |
0.904 |
| 3 |
11974 |
0.84 |
| 4 |
12295 |
1.108 |
| 5 |
12528 |
0.793 |
| 6 |
12601 |
1.285 |
| 7 |
12505 |
0.82 |
| 8 |
11605 |
1.096 |
| 9 |
12410 |
0.901 |
| AVG |
12298.4 |
0.9679 |
5000代
| 序号 |
最优解 |
耗时 / s |
| 0 |
10906 |
3.349 |
| 1 |
11122 |
3.899 |
| 2 |
11265 |
4.49 |
| 3 |
11591 |
5.184 |
| 4 |
11407 |
6.562 |
| 5 |
11282 |
6.531 |
| 6 |
10694 |
6.586 |
| 7 |
11141 |
6.311 |
| 8 |
11663 |
3.579 |
| 9 |
10968 |
7.298 |
| AVG |
11203.9 |
5.3789 |
10000代
| 序号 |
最优解 |
耗时 / s |
| 0 |
10963 |
10.745 |
| 1 |
11278 |
12.68 |
| 2 |
11414 |
14.503 |
| 3 |
10879 |
26.493 |
| 4 |
11010 |
24.973 |
| 5 |
10969 |
37.576 |
| 6 |
11196 |
24.885 |
| 7 |
10977 |
24.884 |
| 8 |
11421 |
17.316 |
| 9 |
10673 |
17.068 |
| AVG |
11078 |
21.1123 |
实验中得到的最优解
点击展开
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| ###################
att48最优解
10628
###################
1
9
40
15
12
11
13
25
14
23
3
22
16
41
34
29
2
26
4
35
45
10
24
42
5
48
39
32
21
47
20
33
46
36
30
43
17
27
19
37
6
28
7
18
44
31
38
8
1
|
Source Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
| #include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <regex>
#include <cmath>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int num, x, y;
};
struct solution {
vector<int> path;
double sum, F, P;
int gen;
};
int curGen = 1;
bool isFound = false;
const int maxGen = 10000;
const int start = 1;
int packNum = 20;
double mutationP = 0.04;
double crossP = 0.7;
double curCost = 0;
int Hayflick = 6;
vector<node> city;
vector<int> num;
vector<solution> pack;
unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, double> > dis;
queue<double> record;
regex pattern("^(\\d+) (\\d+) (\\d+)$");
double distanceBetween(node &a, node &b) {
int x = a.x - b.x;
int y = a.y - b.y;
return ceil(sqrt((x * x + y * y) / 10.0));
}
double sum(vector<int> &v) {
double sum = 0;
for (auto it = v.begin() + 1; it != v.end(); it++) {
sum += dis[*(it - 1)][*it];
}
return sum;
}
bool cmp(const solution &a, const solution &b) {
return a.sum < b.sum;
}
void initData() {
ifstream f("att48.tsp", ios::in);
if (!f) {
cout << "File Not Found" << endl;
}
string s;
while (getline(f, s)) {
if (regex_match(s, pattern)) {
sregex_iterator it(s.begin(), s.end(), pattern);
city.push_back(node{stoi(it->str(1)), stoi(it->str(2)), stoi(it->str(3))});
}
}
f.close();
for (auto it = city.begin(); it != city.end(); it++) {
unordered_map<int, double> temp;
for (auto iterator = city.begin(); iterator != city.end(); iterator++) {
temp[iterator->num] = distanceBetween(*it, *iterator);
}
dis[it->num] = temp;
}
for (auto it = city.begin(); it != city.end(); it++) {
if (it->num != start) {
num.push_back(it->num);
}
}
}
void initPack(int gen) {
for (int i = 0; i < packNum; i++) {
solution temp;
temp.path.push_back(start);
random_shuffle(num.begin(), num.end());
for (auto it = num.begin(); it != num.end(); it++) {
temp.path.push_back(*it);
}
temp.path.push_back(start);
temp.gen = gen;
temp.sum = sum(temp.path);
pack.push_back(temp);
}
if (gen == 1) {
solution greed;
unordered_map<int, bool> isVisited;
greed.path.push_back(start);
isVisited[start] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < num.size(); i++) {
double min = -1;
for (auto it = dis[greed.path.back()].begin(); it != dis[greed.path.back()].end(); it++) {
if (isVisited.count(it->first) == 0 && (min == -1 || it->second < dis[greed.path.back()][min])) {
min = it->first;
}
}
greed.path.push_back(min);
isVisited[min] = true;
}
greed.path.push_back(start);
greed.gen = gen;
greed.sum = sum(greed.path);
pack[0] = greed;
}
}
void passOn() {
record.push(pack[0].sum);
if (record.size() > 500) {
record.pop();
if (curCost != pack[0].sum && record.front() == record.back()) {
vector<int> Prometheus = pack[0].path;
int gen = pack[0].gen;
double sum = pack[0].sum;
pack.clear();
if (Hayflick > 0) {
Hayflick--;
packNum *= log(packNum) / log(10);
}
initPack(gen);
pack[0].path = Prometheus;
pack[0].sum = sum;
sort(pack.begin(), pack.end(), cmp);
curCost = sum;
mutationP += 0.1;
while (!record.empty()) {
record.pop();
}
}
}
}
solution cross(solution &firstParent, solution &secondParent) {
int length = int((rand() % 1000 / 1000.0) * city.size());
int off = rand() % city.size() + 1;
vector<int> nextGen(firstParent.path.size());
unordered_map<int, bool> selected;
nextGen[0] = start;
for (int i = off; i < nextGen.size() - 1 && i < off + length; i++) {
nextGen[i] = firstParent.path[i];
selected[nextGen[i]] = true;
}
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i < nextGen.size(); i++) {
if (nextGen[i] == 0) {
for (; j < secondParent.path.size(); j++) {
if (selected.count(secondParent.path[j]) == 0) {
nextGen[i] = secondParent.path[j];
selected[secondParent.path[j]] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return solution{nextGen, sum(nextGen), 0, 0, firstParent.gen + 1};
}
void mutation(solution &cur) {
int length = int((rand() % 1000 / 1000.0) * city.size());
int off = rand() % city.size() + 1;
vector<int> m;
unordered_map<int, bool> selected;
m.push_back(start);
for (int i = off; i < cur.path.size() - 1 && i < off + length; i++) {
m.push_back(cur.path[i]);
selected[cur.path[i]] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i < cur.path.size(); i++) {
if (selected.count(cur.path[i]) == 0) {
m.push_back(cur.path[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m.size(); i++) {
cur.path[i] = m[i];
}
cur.sum = sum(cur.path);
}
void gmutation(solution &cur) {
int selected = rand() % (city.size() - 4) + 2, min = 1;
int selectedCity = cur.path[selected];
int begin = 0, end = 0;
for (auto it = dis[selectedCity].begin(); it != dis[selectedCity].end(); it++) {
if (it->first != selectedCity && it->second < dis[selectedCity][min]) {
min = it->first;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < cur.path.size() - 1; i++) {
if (cur.path[i] == min) {
if (i > selected + 1) {
begin = selected + 1;
end = i;
} else if (i < selected - 1) {
begin = i;
end = selected - 1;
}
break;
}
}
vector<int> stack;
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
stack.push_back(cur.path[i]);
}
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
cur.path[i] = stack.back();
stack.pop_back();
}
cur.sum = sum(cur.path);
}
vector<solution> process() {
double total = 0;
vector<solution> nextGenPack;
sort(pack.begin(), pack.end() - 1, cmp);
printf("%d %d\n", pack[0].gen, (int) pack[0].sum);
if (pack[0].sum == 10628) {
isFound = true;
}
passOn();
for (auto it = pack.begin(); it != pack.end() - 1; it++) {
it->F = 10000 / it->sum;
it->P = (it == pack.begin() ? 0 : (it - 1)->P) + it->F;
total += it->F;
}
nextGenPack.push_back(pack[0]);
nextGenPack[0].gen++;
for (auto firstParent = pack.begin(); firstParent != pack.end() - 1; firstParent++) {
if (rand() % 10000 / 10000.0 < crossP) {
double selected = (rand() % 10000 / 10000.0) * total;
for (auto secondParent = pack.begin(); secondParent != pack.end() - 1; secondParent++) {
if (selected < secondParent->P) {
nextGenPack.push_back(cross(*firstParent, *secondParent));
break;
}
}
} else {
firstParent->gen++;
nextGenPack.push_back(*firstParent);
}
if (rand() % 10000 / 10000.0 < mutationP) {
Hayflick < 6 ? gmutation(nextGenPack.back()) : mutation(nextGenPack.back());
}
}
return nextGenPack;
}
int main() {
clock_t start = clock();
srand(unsigned(time(NULL)));
initData();
initPack(1);
while (!isFound && curGen <= maxGen) {
pack = process();
curGen++;
}
cout << "Total time: " << double(clock() - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << endl;
cout << "The best: " << pack[0].sum << endl;
for (auto it = pack[0].path.begin(); it != pack[0].path.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|





